Systems Architecture Optimization Using Hidden Genes Genetic Algorithm
In some design optimization problems, it is required to optimize a multi-modal objective function with a variable number of design variables. Most standard optimization algorithms are not suitable for this type of problem.
The Hidden Genes Genetic Algorithms (HGGA) is a biologically inspired concept, developed to handle global optimization problems where the number of design variables is solution dependent.
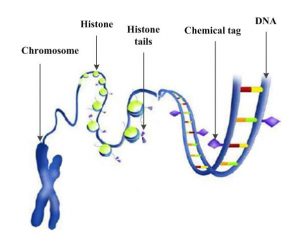
In genetics, biological cells hide the genes that are not supposed to be effective in the cell, while they could be active in another cell. The deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in genetics is organized into a long structure called chromosome (see next Figure). Genes, which are instructions for making a protein, are contained in the DNA and are coded with a specific language with 64 words. Difference in each word, makes genes to produce different proteins, making cells of distinct organs function differently. For example, an eye cell is shut off in the lung and
breathing genes are shut off in the eyes. This duty scheduling is done in another layer of coding in histone which tells genes in a cell what coding they should read and what they should shut off*. This information in the histone about the status of the genes are inheritable to the next generations** and the genes that are shut off are called hidden genes.
In the proposed HGGA, a fixed chromosome length is assumed for all solutions in the population. Each chromosome is divided into effective and ineffective segments. The effective segment in a chromosome includes the design variables for that solution. The ineffective segment includes only hidden genes. Hidden genes are excluded in objective function evaluations. Full chromosomes undergo standard genetic operations.

Watch a short video on HGGA
Relevant Publications
- Ossama Abdelkhalik. Algorithms for Variable-Size Optimization: Applications in Space Systems and Renewable Energy (1st ed.). CRC Press. April 2021. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781351119108
- Shadi Darani and Ossama Abdelkhalik, Space Trajectory Optimization Using Hidden-Genes Genetic Algorithms, AIAA Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, Vol. 55, No. 3, pp. 764-774, 2018, https://doi.org/10.2514/1.A33994.
- Ossama Abdelkhalik, and Shadi Darani, Evolving Hidden Genes in Genetic Algorithms for Systems Architecture Optimization, ASME Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement and Control, Vol. 140, No. 10, pp. 101015-1 — 101015-11, October 2018 (online in June 2018).
- Shadi Darani and Ossama Abdelkhalik, Convergence Analysis of Hidden Genes Genetic Algorithms in Space Trajectory Optimization, AIAA Journal of Aerospace Information Systems, Vol. 15, No. 4, pp. 228-238, April 2018,
http://arc.aiaa.org/doi/abs/10.2514/1.I010564 - Shadi Darani, Casey D. Majhor, Wayne Weaver, Rush D. Robinett, Ossama Abdelkhalik. Optimal Positioning of Energy Assets in Autonomous Robotic Microgrids for Power Restoration, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, special issue on Resilience in Energy Industries – Recent Advances, Open Challenges, and Future Directions, Vol. 15, No. 7, pp. 4370-4380, July 2019.
- Ossama Abdelkhalik, and Shadi Darani, Optimization of Nonlinear Wave Energy Converters, Ocean Engineering, Elsevier, Vol. 162, pp. 187–195, May 2018 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0029801818307881
- O. Abdelkhalik, Hidden Genes Genetic Optimization for Variable-Size Design Space Problems. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, Springer, Volume 156, Number 2, 2013.
- Ossama Abdelkhalik, and Shadi Darani. Hidden Genes Genetic Algorithms for Systems Architecture Optimization. ACM Proceedings, Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference, GECCO ’16, July 20–24, 2016, Denver, CO, USA. http://http//dx.doi.org/10.1145/2908812.2908819
- Shadi Darani and Ossama Abdelkhalik, Developments on The Optimization of Interplanetary Trajectories using Hidden Genes Genetic Algorithms. AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference, Long Beach, California, 13 – 16 September 2016.
Broader Applications
- Numerical simulation and optimization models for socio-dynamical features of crowd evacuation: Link
Acknowledgment
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant Number 1446622
Disclaimer
Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
________________________________________________________________________________________________
* Barry Starr. Spooled dna and hidden genes: The latest finding in how our DNA is organized and read. The Tech Museum of Innovation, Department of Genetics, Stanford School of Medicine, 201 South Market Street San Jose, CA 95113. http://www.thetech.org/genetics/news.php?id=31.
** Bryan M. Turner. Histone acetylation and an epigenetic code. Bioessays, 22:836–845., September 2000.